Cloud Computing
Cloud processing
The increasing advancement of technology and the need for easy access to the required infrastructure at a lower cost led to the creation of cloud computing technology.
What is cloud computing?

Today, with the advancements in technology and the need to perform processing tasks anytime and anywhere, there is a requirement for services that allow individuals to do their work easily without the need to purchase expensive hardware and software. For this reason, a technology called cloud computing was developed.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines cloud computing as: "A model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (such as networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction."
Usually, cloud users are not the physical owners of the cloud; instead, they obtain the resources they need from cloud providers and only pay for the resources used. Cloud computing enables the consumption of services in a manner similar to public utilities (such as electricity), where we only pay for the electricity we consume.
A Difficult Beginning with a Sweet Ending
After years of skepticism and widespread distrust among experts, cloud computing has finally established itself as the definitive and unstoppable trend for using software applications. Currently, the main barriers to its widespread adoption are rapidly being addressed.
The traditional barriers to the acceptance of cloud computing include:
- Technical requirements
- Operational reliability
- Data privacy protection
- User lack of control over cloud features
- Provider responsibility
- Intellectual property rights
To achieve proper adoption of cloud computing in the short term, the following necessities must be observed:
Reliability: This application should not fail, shut down, cause data disturbances, or disappear. Cloud providers must guarantee hardware and software reliability and offer a completely secure system in terms of architecture, redundancy, and fault tolerance.
Privacy: Information must be kept confidential, and nobody should access it without identification. Cloud means a place where many customers share resources like hardware and software to reduce costs for each use. Therefore, privacy for each customer should be maintained with a private and separate database.
Legal conditions: All issues related to provider responsibilities, termination rights, and intellectual property rights must be clearly specified in the contractual terms.
Today, it appears that all the above issues have practically been resolved, and therefore it is expected that cloud computing will expand and penetrate in most activities and many fields in the coming years.
What tools do users need?
The only device a user needs to access cloud services is a terminal such as a workstation, a personal computer, a tablet, or a smartphone with internet access. That’s all!
Three-tier service in cloud computing
Cloud computing includes three levels of services, all of which are provided by cloud providers.
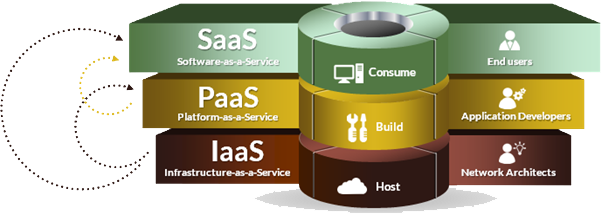
IaaS
The first level is called IaaS, or Infrastructure as a Service.
At this level, the cloud provider facilitates the use of hardware and software systems that any user may need for processing and storage capacity.
This includes cooling systems and a risk-free location for the entire system, as well as ensuring high performance, high-bandwidth internet connectivity, and maintenance.
This service level allows customers to deploy their applications and operating systems in the cloud provider's data center, but it does not supply or maintain the applications themselves.
PaaS
The second level, PaaS, or Platform as a Service, is a software platform offering.
The cloud provider facilitates the development of the software platform. Therefore, developers may create applications using appropriate programming languages and integrated development environments.
This level guarantees the performance and maintenance of the platform components but does not guarantee the performance and maintenance of the developed applications.
SaaS
The third level, SaaS, or Software as a Service, is a cloud service offering.
This level includes ready-to-use applications, guarantees their performance, and ensures the maintenance of the provided applications, including updates.
An end-user simply needs an application to access the software via SaaS and the hardware infrastructure provided by IaaS, where the software resides, but does not need the PaaS level.
The PaaS level is suitable for users who intend to develop applications using the development platform offered by the cloud provider.





